最近一直在跟踪大模型的事情,热度很高,每次开会不提大模型都显得不接地气,但是大模型看来看去依然存在AI的通病:不是100%准确;更无法解释。大模型短期内还是无法替代人类,但是已经可以更好的辅助辅助人类开展各项工作了。在热度之下,就要有个清醒的定位。华为在7月7日发布的盘古大模型,考虑到华为是全栈技术,可能和其他公司发布的大模型有些不一样,简单调研了一下盘古的历程,以及几个重要的基础模型,特别是被《Nature》收录的《Accurate medium-range global weather forecasting with 3D neural networks》。
一、盘古大模型发展简史
华为盘古大模型的创始人是田齐(现任华为云人工智能领域首席科学家),田齐团队一开始选择和NLP和CV两个赛道;确立了三项核心设计原则:一是模型要大,可吸收海量的数据;二是网络结构要强,能够真正发挥出模型的性能;三是要具有优秀的泛化能力,可以真正落地到各行各业的工作场景。这些选择一方面是华为在AI领域已经深耕多年,全栈技术,积累多,资源多,起步高;另外一方面,对于技术和行业的预判相当准确,在几年前就开展了务实的行业布局(做事)。
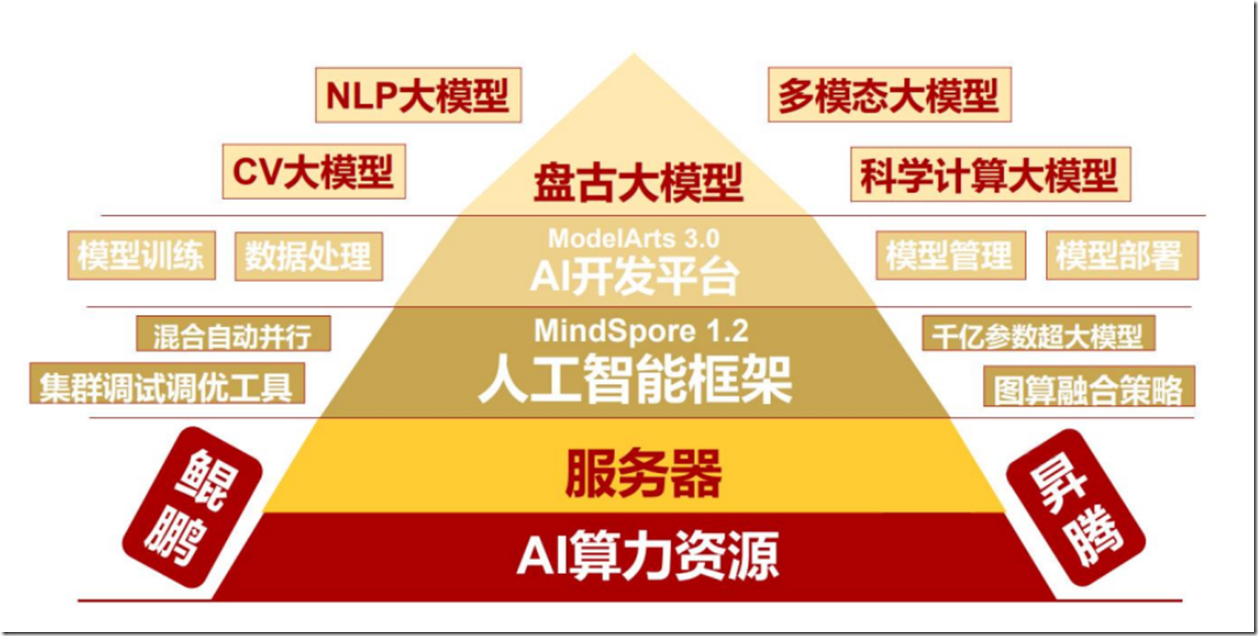
华为盘古大模型构成(互联网图片)
2020年3月,田奇(华为云人工智能领域首席科学家、IEEE Fellow)加入华为云后便开始组建团队,并且进行了方向梳理;8月,团队迎来新的核心专家;9月,团队开始推动盘古大模型的立项,希望能够在华为云的产业基座上,完成适配各个产业AI开发的大模型;11月,盘古大模型在华为云内部立项成功,并完成了与合作伙伴、高校的合作搭建。
2021年4月25日,在华为开发者大会上,余承东发布了盘古系列超大规模预训练模型,包括 30 亿参数的视觉(CV)预训练模型,以及与循环智能、鹏城实验室联合开发的千亿参数、40TB 训练数据的中文语言(NLP)预训练模型。华为云盘古NLP大模型在中文语言理解测评中,在总榜、分类榜、阅读理解榜获得三项第一,大幅刷新业界纪录。总排行榜领先第二名1分。盘古团队:1000亿参数NLP+CV,20多名博士、30多名工程师、3名广受关注的“华为天才少年”,还有50多名来自全国C9高校的专家。
2021年4月26日,鹏城实验室联合有关单位发布「盘古α」,这是业界首个2000亿参数中文预训练语言模型!模型使用国产全栈式软硬件协同生态(MindSpore+CANN+昇腾910+ModelArts),基于“鹏城云脑Ⅱ”和MindSpore框架的自动混合并行模式实现在2048卡算力集群上的大规模分布式训练。
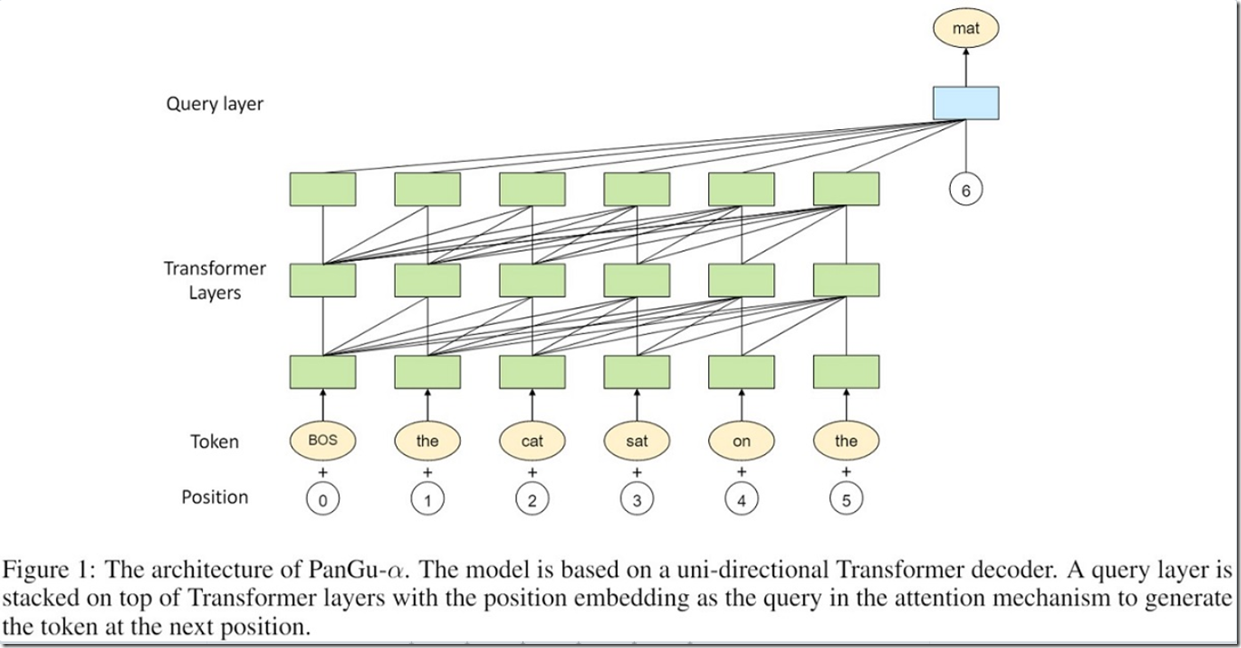
盘古α技术逻辑架构
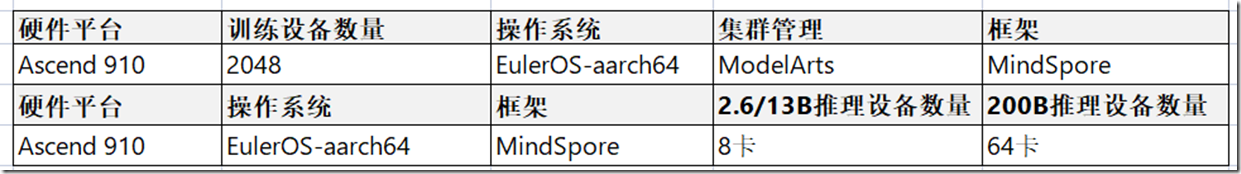
盘古α的训练和推理技术栈
2021年9月23日,华为全联接2021大会上,华为高级副总裁、华为云CEO、消费者云服务总裁张平安发表“深耕数字化,一切皆服务”主题演讲,并重磅发布了华为云盘古药物分子大模型华为云发布了盘古药物分析大模型。华为云联合中国科学院上海药物研究所,共同训练了华为云盘古药物分子大模型。此模型对市面上真实存在的17亿个药物分子的化学结构进行预训练,在化学无监督学习模式下,实现结构重构率、合法性、唯一性等指标全面优于现有方法。盘古药物分子大模型首次采用“图-序列不对称条件变分自编码器”架构, 可以自动找出化合物关键的分子特征指纹,极大地提升了下游任务的准确性。盘古药物分子大模型的分子生成器生成了1亿个创新的类药物小分子筛选库,其结构新颖性为99.68%。此模型依托华为云医疗智能体EIHealth平台。
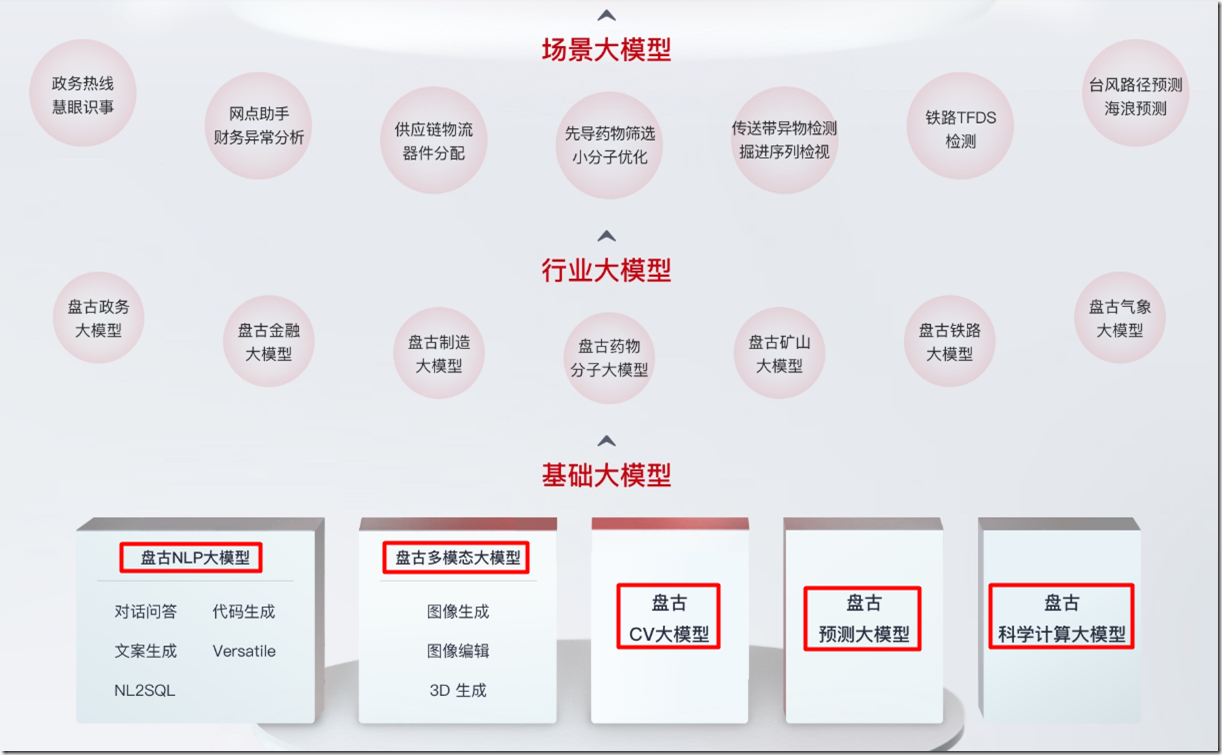
2022年8月16日,可信AI峰会在北京举办。华为云盘古预训练大模型通过中国信通院首轮大模型测评,在“模型开发”和“模型能力”两部分达到4+级标准。华为云人工智能领域首席科学家、IEEE Fellow、国际欧亚科学院院士田奇发表主题演讲。他表示,华为云盘古预训练大模型不断迭代,形成了“L0基础大模型-L1行业大模型-L2细分场景大模型”的发展路径,完成从学术大模型到产业大模型的转变。
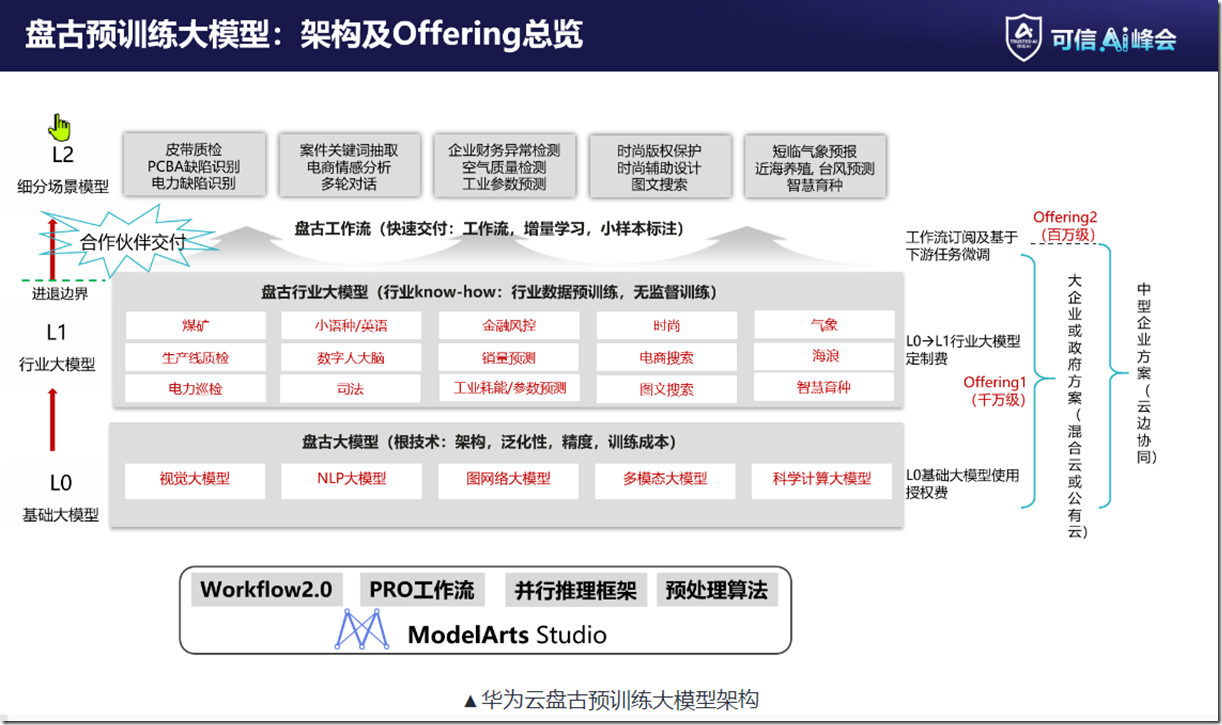
华为云盘古预训练大模型架构(2022年可信AI峰会)
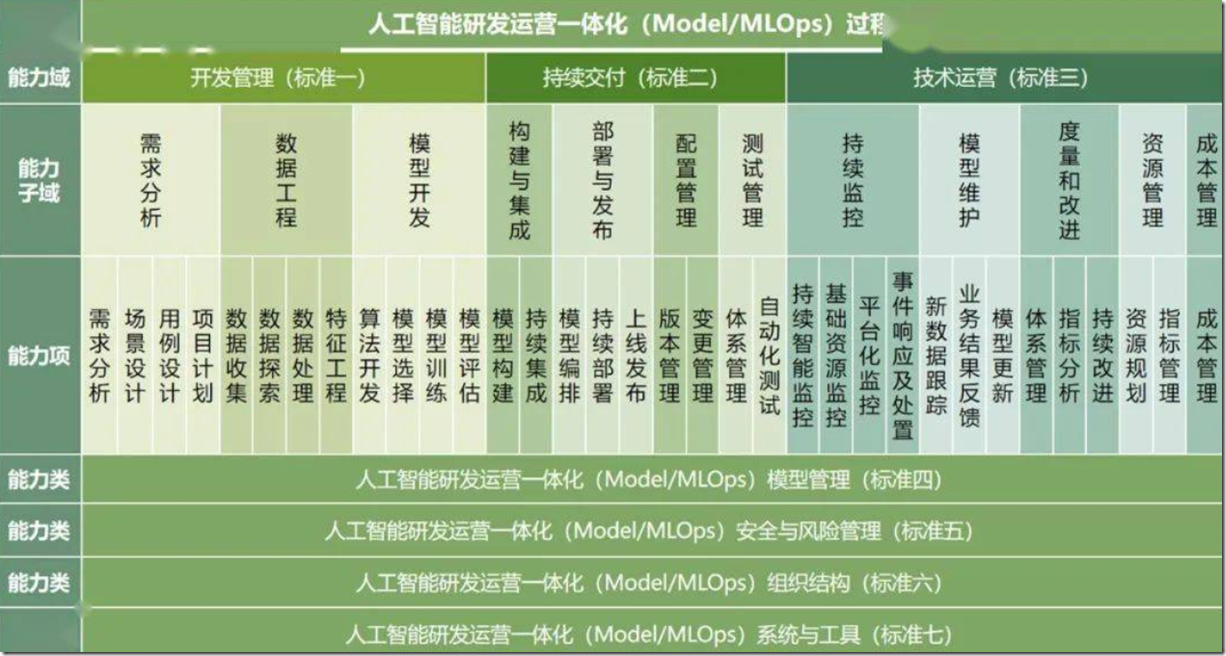
《人工智能研发运营一体化(Model/MLOps)能力成熟度模型》标准体系(互联网)
能力成熟度等级划分(互联网)
2022年9月1日,华为轮值董事长胡厚崑在2022世界人工智能大会上表示,人工智能触发的产业变革正在改变每一个行业,人工智能也在越来越多的行业场景发挥重要价值。基于华为云盘古预训练大模型打造的华为云AI辅助药物设计平台(Huawei Cloud AI Drug Design Platform)获得了“SAIL之星”奖项。Drug X有望成为全球近40年来首个新靶点、新类别的抗生素,其靶点特质决定了细菌将难以对Drug X产生耐药性,对抗疟(即疟原虫)药物研发等多个领域有着重要的影响。华为云盘古药物分子大模型让先导药的研发周期从数年缩短至一个月,研发成本降低70%
2022年11月7日,华为全联接大会 2022 中国站上,华为云田齐进一步迭代盘古大模型的技术能力,扩展盘古大模型的服务范围,发布盘古气象大模型、盘古海浪大模型、盘古矿山大模型、盘古OCR大模型等重磅服务。华为云发布《预训练大模型白皮书》。
扫描二维码可以下载白皮书,但是在华为白皮书网站找不到
2023年4月8日,人工智能大模型技术高峰论坛,华为田齐展示古系列 AI 大模型:NLP大模型、CV 大模型、科学计算大模型(气象大模型)、多模态大模型、语音大模型等多个模型
2023年7月5日,国际顶刊Nature登载了华为云盘古气象大模型研发团队研究成果,成为近年来首篇以中国科技公司为唯一署名单位发表的Nature正刊论文。审稿人高度评价该模型:“华为云盘古气象大模型让人们开始重新审视气象预报模型的未来,模型的开放将推动该领域的发展。”作为首个精度超过传统数值预报方法的AI预测模型,盘古气象大模型的预测速度也有大幅提升。原来预测一个台风未来10天的路径,需要在3000台服务器的高性能计算机集群上花费5小时进行仿真。现在基于预训练的盘古气象大模型,通过AI推理的方式,研究者只需单台服务器上单卡配置,10秒内就可以获得更精确的预测结果。
2023年7月7日,华为开发者大会(HDC 2023),华为云CEO张平安正式对外发布了盘古大模型3.0。第一是”不作诗,只做事”。第二是“ALL in AI”。盘古大模型 3.0 包括「5+N+X」三层架构,三层分别指 L0 层的 5 个基础大模型、L1 层的 N 个行业通用大模型、以及 L2 层可以让用户自主训练的更多细化场景模型。张平安宣布单集群 2000P Flops 算力的昇腾 AI 云服务在华为云的乌兰察布和贵安 AI 算力中心同时上线。昇腾 AI 云服务除了支持华为全场景 AI 框架昇思 MindSpore 外,还支持 Pytorch、Tensorflow 等主流 AI 框架。昇腾 AI 云服务可以提供更长稳的 AI 算力服务,千卡训练 30 天长稳率达到 90%,断点恢复时长不超过 10 分钟
盘古大模型 3.0 是一个面向行业的大模型系列,包括「5+N+X」三层架构(华为大会)
五个基础大模型:包括自然语言、视觉、多模态、预测、科学计算大模型。盘古 3.0 为客户提供 100 亿参数、380 亿参数、710 参数和 1000 亿参数的系列化基础大模型(华为网站)
盘古大模型全栈技术(华为大会)
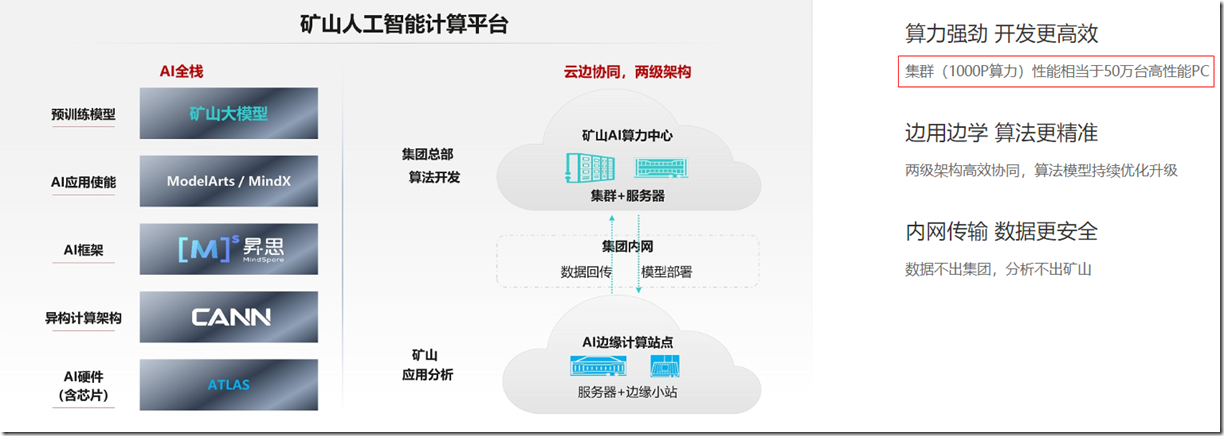
2023年7月18日,山东能源集团、华为公司联合发布全球首个商用于能源行业的AI大模型——盘古矿山大模型。该模型将凭借“经营管理与智能生产分离”“数据不出园区”“支持规模复制”“学习分析小样本”等能力特性。煤矿领域,盘古矿山大模型已经在全国8个矿井规模使用,一个大模型可以覆盖煤矿的采、掘、机、运、通、洗选等业务流程下的1000多个细分场景,让更多的煤矿工人能够在地面上作业,不仅能让煤矿工人的工作环境更加舒适,而且可以极大地减少安全事故
华为盘古矿山大模型,需要注意这是一个私有化部署(华为网站)
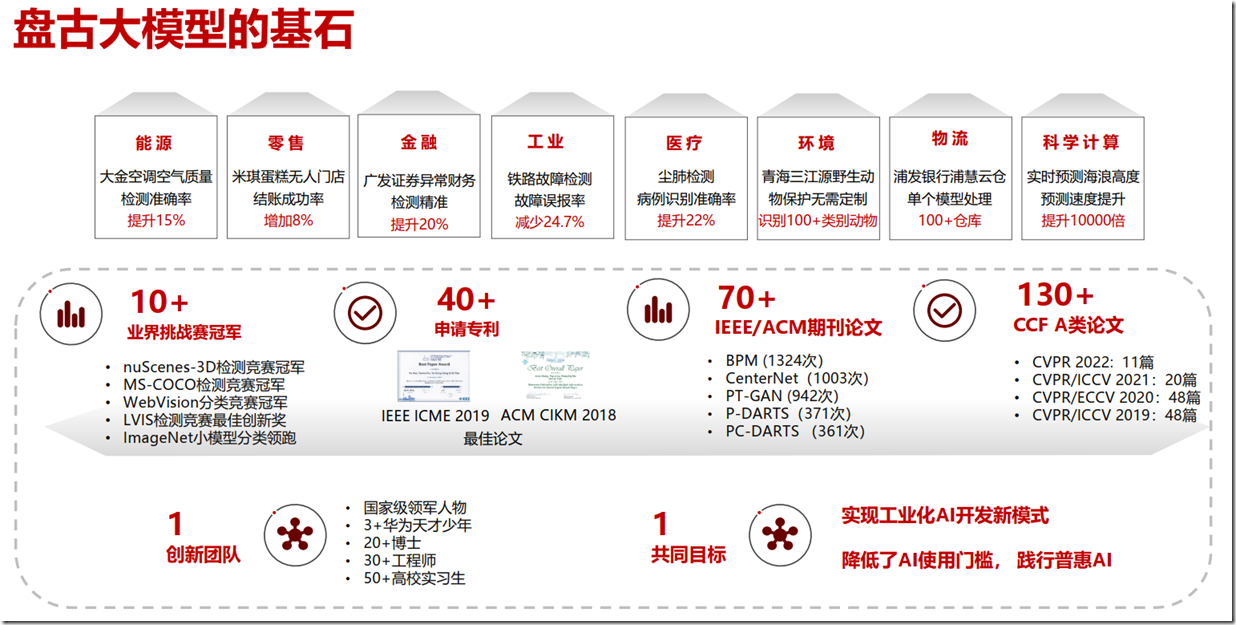
华为大模型基石(华为网络材料)
二、盘古科学计算大模型
盘古3.0发布前,华为发布了一个《预训练大模型白皮书》,这个白皮书中介绍了科学计算大模型的一些内容,摘录部分,有助于理解其内涵。
在人工智能之前,科学家们通常通过分析实验数据与推演机理公式的方式提炼自然科学问题(湍流模拟、天气预报、大形变应力等)的内在规律。这些传统方法,容易在大体量、高维度的数据处理上遇到困难。近年来,随着人工智能技术的飞速发展,业界涌现出了 AI+ 科学计算类方法,即使用嵌入各类科学方程的深度神经网络,从观测数据和仿真数据中直接学习问题蕴含的规律,以对复杂的科学数据进行分析,了解科学过程的内部机理。从预训练大模型的角度看,科学计算大模型与NLP、CV等大模型存在若干相似之处。它们都建立在大规模数据集上,都需要设计大参数量的神经网络,都需要复杂的优化过程,最后将知识存储在网络的参数之中。
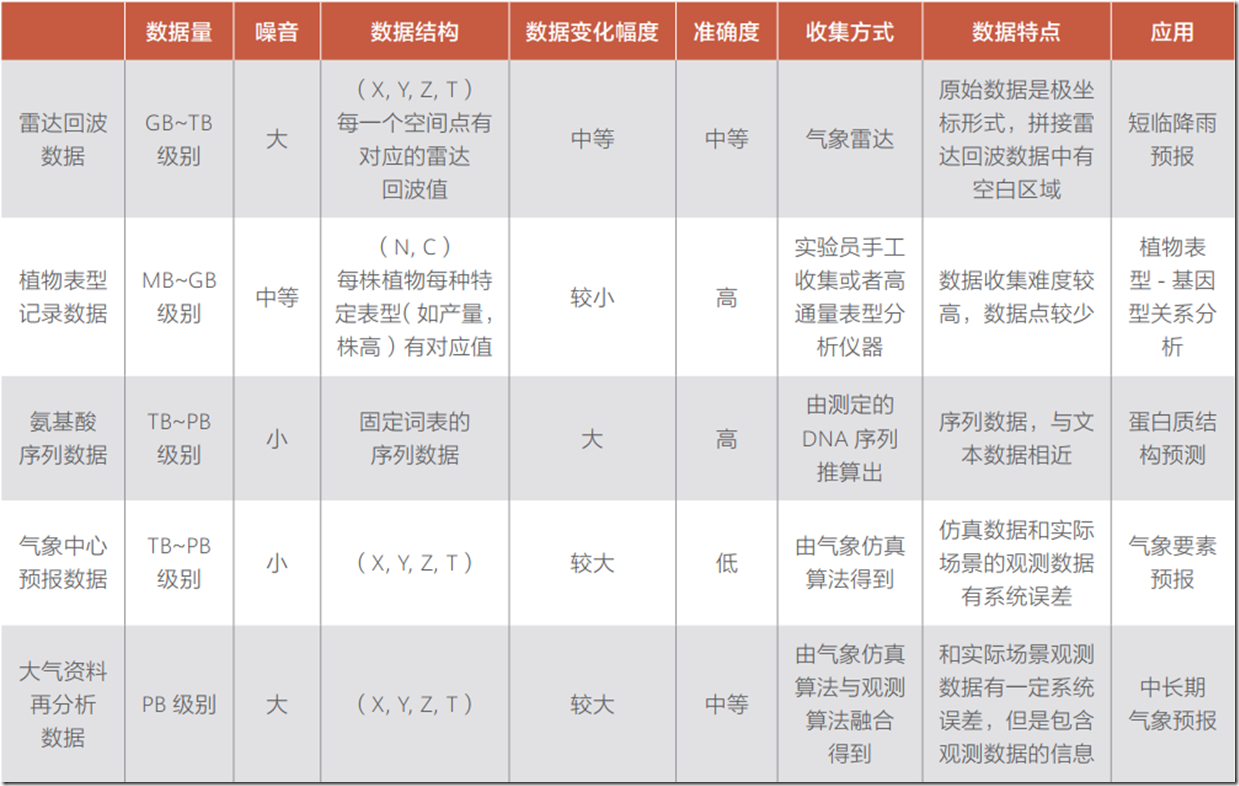
1、数据来源。不同科学计算场景的观测数据往往相差巨大,观测数据的收集往往需要特定领域的专业仪器与系统的实验,例如蛋白质结构预测问题中蛋白质结构的测定需要依赖于 X 射线衍射方法与核磁共振法、短临降雨预报问题中需要气象雷达收集的雷达波反射率数据、植物表型分析问题中数据则来自于实验员的收集,等等。在一些科学计算场景中,观测数据的数据量非常庞大,例如气象数据中的全球气象站历史数据、卫星数据和雷达回波数据。也有一些场景中,观测数据量相对较少,例如结构应力分析力传感器收集的数据。
仿真数据来自于数值仿真算法的输出,蕴含着丰富的数学物理信息,同一个问题使用不同的仿真算法可以输出不同的仿真数据。仿真数据不同于观测数据,其精度受限于使用仿真算法的准确性和仿真计算的算力多少。相对于观测数据,仿真数据通常数据量更大(取决于仿真时使用的算力),同时缺省值较少,可以作为观测数据的有效扩充。有些场景中,观测数据和仿真数据由特定的机理知识结合在一起,生成融合数据。如气象再分析数据,再分析数据通常使用同化算法融合仿真数据和实验数据得到结构化的数据,根据不同同化算法与使用的仿真数据也可以有不同的结果。
2、模型构建。根据输入数据的性质,算法会选用不同的基础模型用于训练。以海浪预测任务为例,其目标为预测全球范围内海平面的实时浪高,输入和输出数据均为带有时间戳的二维球面数据,因此适合使用二维网络模型。如果将预测范围扩展至三维空间,如进行全球范围内的气象预测,输出和输出均为带有时间戳的三维数据(包括高度),则适合使用三维网络模型。二维网络和三维网络均可以借鉴计算机视觉领域的相应模型,如使用卷积神经网络或者视觉 Transformer 作为骨干架构,配合大数据进行预训练。
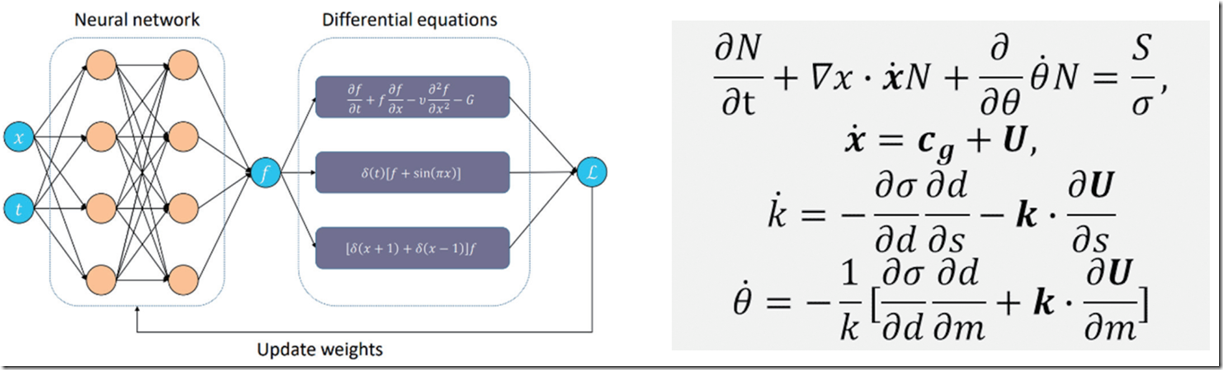
科学计算的一个显著特点,是可以利用人类在相应问题上积累的经验,而这些经验通常会施加在输出数据上,成为某种约束性质的偏微分方程组。如下图所示,我们可以将此类方程组嵌入神经网络中,辅助模型架构设计或成为额外的约束条件,与标准观测或仿真数据一起,训练神经网络模型。在良好的实现下,这类知识通常能够增强模型的鲁棒性,降低模型拟合训练数据的难度和不稳定性。
左图为嵌入偏微分方程的神经网络示意图,右图为海浪预报问题使用的偏微分方程
3、海浪大模型。海浪预测问题的输入输出都是经纬度网格点上的气象要素数据,在数据形式上与视频数据相似。不同之处在于,视频数据每个元数据是 0-255 的像素值,而风速、地形、海浪高度等数据的每个元数据均为浮点数。同时,海浪预测的输出通常不是某种分类,而是连续的预测值,因此需要用回归损失替换深度学习中常用的分类、分割损失。此外,海浪数据和视频数据相比,并不满足平移对称性等,但满足球坐标条件下的一系列不变性,例如绕地轴旋转,因此需要选定满足特定不变性的 CNN 或者 Transformer 架构。
盘古海浪预测模型的主体是考虑了旋转不变性的视觉 Transformer 架构,参数量约为五亿。如上所述,神经网络的损失函数由两部分组成,即实际数据上的预测误差和海浪预测本身需要满足的偏微分方程。通过爬取全球近10年的实时海浪高度数据进行训练,模型在验证集上预测的平均误差小于5cm,与传统预测方法相当,完全可以满足实际应用需求。更重要的是, AI 算法的预测时间较传统方法大幅减少:在单张华为昇腾芯片上,1s 之内即可得到全球海浪高度预测, 1 分钟内能够完成超过 100 次海浪预测任务,推理效率较传统方法提升了 4-5 个数量级。使用 AI 算法,我们可以迅速得到不同可能的风速条件下的海浪高度,从而进行实时预测和未来情况模拟,对于渔业养殖、灾害防控等场景有极大的价值。
三、《Accurate medium-range global weather forecasting with 3D neural networks》
在华为的模型体系中,气象大模型是L1层,而台风预测和海浪预测则是L2层,这种分层在逻辑上有其价值,但是看上去未必有L2大模型,更像是L1模型的应用。摘录一些论文内容,英文的看的更明白。
In the past decade, high-performance computing systems have greatly accelerated research in the field of numerical weather prediction (NWP) methods. Conventional NWP methods are primarily concerned with describing the transitions between discretized grids of atmospheric states using partial differential equations (PDEs) and then solving them with numerical simulations. These methods are often slow; a single simulation for a ten-day forecast can take hours of computation in a supercomputer that has hundreds of nodes. In addition, conventional NWP algorithms largely rely on parameterization, which uses approximate functions to capture unresolved processes, where errors can be introduced by approximation. (传统方法是利用超算解偏微分方程)
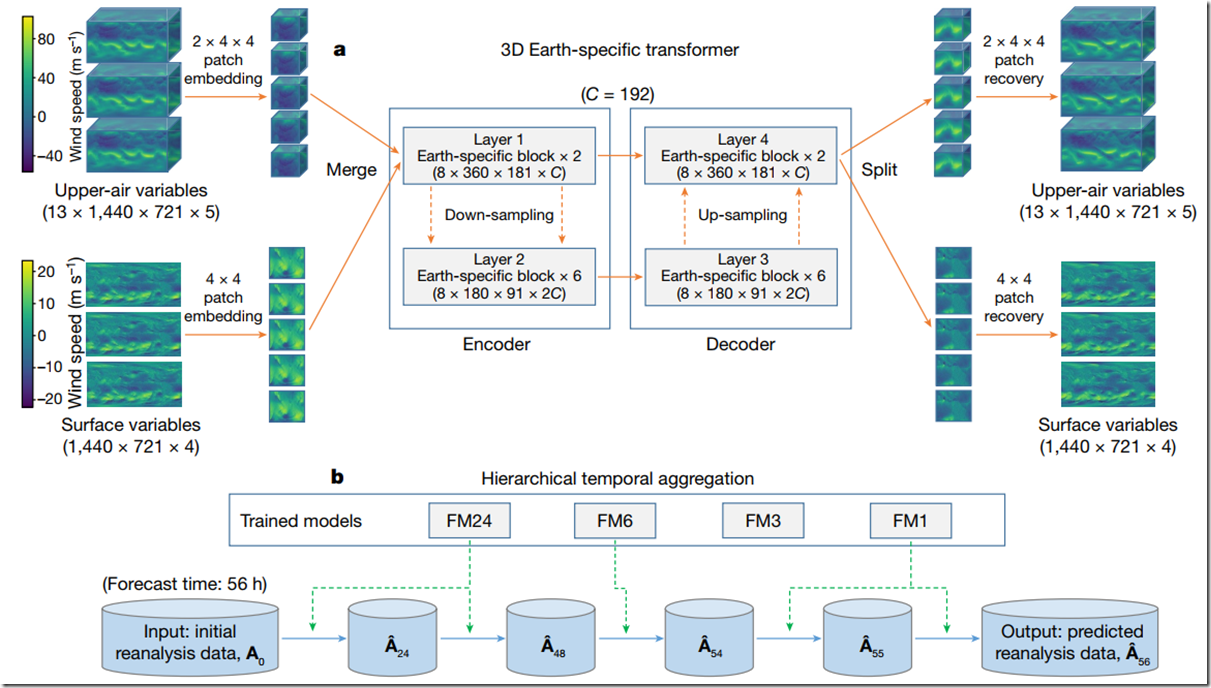
First, we integrated height information into a new dimension so that the input and output of our deep neural networks can be conceptualized in three dimensions. We further designed a three-dimensional (3D) Earth-specific transformer (3DEST) architecture to inject Earth-specific priors into the deep networks. Our experiments show that 3D models, by formulating height into an individual dimension, have the ability to capture the relationship between atmospheric states in different pressure levels and thus yield significant accuracy gains, compared with two-dimensional models such as FourCastNet. Second, we applied a hierarchical temporal aggregation algorithm that involves training a series of models with increasing forecast lead times. Hence, in the testing stage, the number of iterations needed for medium-range weather forecasting was largely reduced, and the cumulative forecast errors were alleviated. Experiments on the fifth generation of ECMWF reanalysis (ERA5) data18 validated that Pangu-Weather is good at deterministic forecast and extreme weather forecast while being more than 10,000-times faster than the operational IFS ( integrated forecasting system). (两大贡献,其中提升精度依靠了3D建模、提升预测能力采用了4个模型)
We established our weather forecast system via deep learning. The methodology involves training deep neural networks to take reanalysis weather data at a given point in time as input, and then produce reanalysis weather data at a future point in time as output. We used a single point in time for both input and output. The time resolution of the ERA5 data is 1 h; in the training subset (1979–2017), there were as many as 341,880 time points, the amount of training data in one epoch. To alleviate the risk of over-fitting, we randomly permuted the order of sample from the training data at the start of each epoch. We trained four deep networks with lead times (the time difference between input and output) at 1 h, 3 h, 6 h and 24 h, respectively. Each of the four deep networks was trained for 100 epochs, and each of them takes approximately 16 days on a cluster of 192 NVIDIA Tesla-V100 GPUs.(注意:使用了Nvidia的V100卡,不是A100也不是昇腾)
3DEST architecture. Based on the standard encoder–decoder design of vision transformers, we adjusted the shifted-window mechanism19 and applied an Earth-specific positional bias. b, Hierarchical temporal aggregation. Once given a lead time, we used a greedy algorithm to perform forecasting with as few steps as possible. We use FM1, FM3, FM6 and FM24 to indicate the forecast models with lead times being 1 h, 3 h, 6 h or 24 h, respectively. A0 is the input weather state and A^A^t denotes the predicted weather state at time t (in hours).
This architecture is known as the 3D Earth-specific transformer (3DEST). We fed all included weather variables, including 13 layers of upper-air variables and the surface variables, into a single deep network. We then performed patch embedding to reduce the spatial resolution and combined the down-sampled data into a 3D cube. The 3D data are propagated through an encoder–decoder architecture derived from the Swin transformer19(微软亚洲院提出的模型,针对CV识别做了窗口、平移和批处理优化), a variant of a vision transformer20, which has 16 blocks. The output is split into upper-air variables and surface variables and is up-sampled with patch recovery to restore the original resolution. To inject Earth-specific priors into the deep network, we designed an Earth-specific positional bias (a mechanism of encoding the position of each unit; detailed in Methods) to replace the original relative positional bias of Swin. This modification increases the number of bias parameters by a factor of 527, with each 3D deep network containing approximately 64 million parameters. Compared with the baseline, however, 3DEST has the same computational cost and has a faster convergence speed. (毕竟是一个多层的气象球体,采用图像分块处理没毛病)
The lead time of a medium-range weather forecast is 7 days or longer. This prompted us to call the base deep networks (lead times being 1 h, 3 h, 6 h or 24 h) iteratively, using each forecasted result as the input of the next step. To reduce the cumulative forecast errors, we introduced hierarchical temporal aggregation, a greedy algorithm that always calls for the deep network with the largest affordable lead time. Mathematically, this greatly reduces the number of iterations. As an example, when the lead time was 56 h, we would execute the 24-hour forecast model 2 times, the 6-hour forecast model 1 time, and the 1-hour forecast model 2 times (Fig. 1b). Compared with FourCastNet2, which uses a fixed 6-hour forecast model, our method is faster and more accurate. The limitation of this strategy is discussed in Methods. (这是对模型的使用)
To fairly compare Pangu-Weather against FourCastNet2, we trained our 3D deep networks on 39 years of data (from 1979 to 2017), validated them on 2019 data and tested them on 2018 data. We studied 69 factors, including 5 upper-air variables at 13 pressure levels (50 hPa, 100 hPa, 150 hPa, 200 hPa, 250 hPa, 300 hPa, 400 hPa, 500 hPa, 600 hPa, 700 hPa, 850 hPa, 925 hPa and 1,000 hPa) and 4 surface variables. When tested against reanalysis data, for each tested variable, Pangu-Weather produces a lower RMSE and a higher anomaly correlation coefficient (ACC) than the operational IFS and FourCastNet, the best NWP and AI-based methods, respectively. (这部分需要气象学知识了)
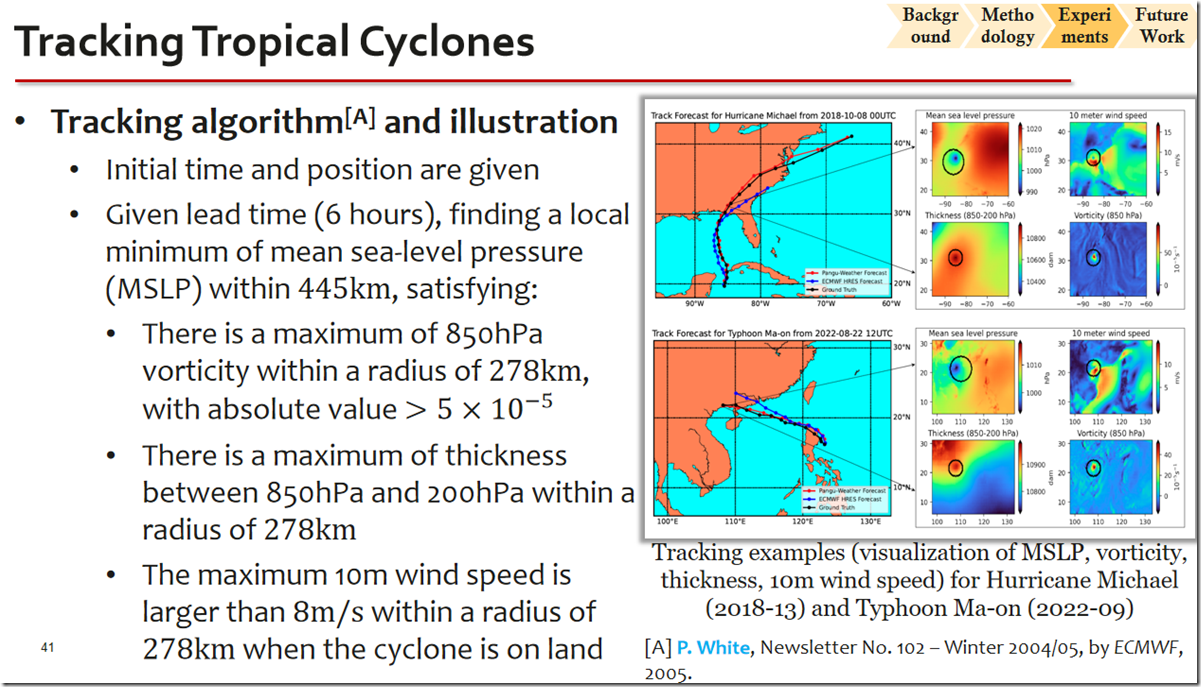
【台风轨迹】Next, we used Pangu-Weather to track tropical cyclones. Given an initial time point, we set the lead time to be multiples of 6 h (ref. 23) and initiated Pangu-Weather to forecast future weather states. We looked for the local minimum of MSLP that satisfied certain conditions, such as the cyclone eye. The tracking algorithm is described in the supplementary material for this paper. We used the International Best Track Archive for Climate Stewardship (IBTrACS) project24,25, which contains the best available estimations for tropical cyclones.
We compared Pangu-Weather with ECMWF-HRES, a strong cyclone tracking method based on high-resolution (9 km × 9 km) operational weather forecasting. We chose 88 named tropical cyclones in 2018 that appear in both IBTrACS and ECMWF-HRES. As shown in Fig. 4, Pangu-Weather statistically produced more accurate tracking results than ECMWF-HRES for these cyclones. The 3-day and 5-day mean direct position errors for cyclone eyes were reported at 120.29 km and 195.65 km for Pangu-Weather, which are smaller than 162.28 km and 272.10 km for ECMWF-HRES, respectively. The breakdowns of tracking errors with respect to regions and intensities are provided in Extended Data Fig. 5. The advantage of Pangu-Weather becomes more significant as the lead time increases. We also show the tracking results of the two strongest cyclones in the western Pacific, Kong-rey and Yutu, in Fig. 4. See the supplementary material for a detailed analysis.
【推理速度】The inference speed of Pangu-Weather is comparable to that of FourCastNet2. In a system-level comparison, FourCastNet requires 0.28 s for inferring a 24-hour forecast on a Tesla-A100 GPU (312 teraFLOPS), whereas Pangu-Weather needs 1.4 s on a Tesla-V100 GPU (120 teraFLOPS). Taking GPU performance into consideration, Pangu-Weather is about 50% slower than FourCastNet. Pangu-Weather is more than 10,000-times faster than the operational IFS, which requires several hours in a supercomputer with hundreds of nodes.
【盘古由来】Pangu is a primordial being and creation figure in Chinese mythology who separated heaven and earth and became geographic features such as mountains and rivers (see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pangu). Pangu is also a series of pre-trained AI models developed by Huawei Cloud that covers computer vision, natural language processing, multimodal understanding, scientific computing (including weather forecasting) and so on.
【预训练模型】We released the trained models, inference code and the pseudocode of details to the public at a GitHub repository: https://github.com/198808xc/Pangu-Weather (https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7678849).
【演讲材料】 https://pan.baidu.com/s/14ZGywcr4XAK5dk75-8PUqA?pwd=9sco
模型的详细介绍可以看原文:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-06185-3
小结:
看看论文原文有助于辨别一些网上自媒体软文的误导,3DEST是一个基于前人工作基础的创新,把数据分层提升了预测精度,而训练不同时间段的模型虽然不够优雅,但是解决中期气象预测的中可能造成的累计误差,提升了结果的准确性。能够登上Nature的原因不是因为模型有多先进,是工程化和算法的协同创新,解决了预测领域的实际问题,结果还特别好。华为在一些宣传中把气象预测大模型和昇腾卡一起介绍,多少有些误导,这还是用V100训练的。同时把各种大模型分成L0-L1-L2也有些过拟合,感觉L0应该是Transformer,然后才是基础大模型和微调大模型。当然这里面存在商业宣传方面的诉求,毕竟让普通客户看懂最为重要。
大模型肯定还会热很久,寻找自己的位置并坚持创新是华为盘古大模型取得成功的经验!
相关信息:
Accurate medium-range global weather forecasting with 3D neural networks
https://openi.pcl.ac.cn/PCL-Platform.Intelligence/PanGu-Alpha
6000 字详解华为盘古大模型:能否撑起世界 AI 另一极?
华为盘古大模型新进展,华为云AI首席科学家7000字演讲精华
余承东新身份首秀:华为云发布全球最大盘古大模型,2.2亿美元培育沃土
华为“盘古气象”登上Nature!比全球最好数值天气预报系统更准确,速度还快10000倍
直击WAIC 2022 丨 华为云盘古大模型加速AI在千行百业的孵化与创新
【大厂内参】第16期:华为云AI开发生产线,破解AI全流程开发难题
视觉大模型调研(Survey of Visual Foundation Model)
干货分享|HDC 2022 开发者主题演讲与技术分论坛PPT汇总(建议收藏)
华为云提出盘古气象大模型:中长期气象预报精度首次超过传统数值方法,速度提升10000倍以上
HDC.Cloud 2021 | 华为云发布全球最大预训练模型,开启工业化AI开发新模式
中国信通院发布《人工智能研发运营一体化(Model/MLOps)能力成熟度模型》标准体系





可以谈谈最新的华为手机 7nm 芯片?
这个芯片目前层层迷雾!